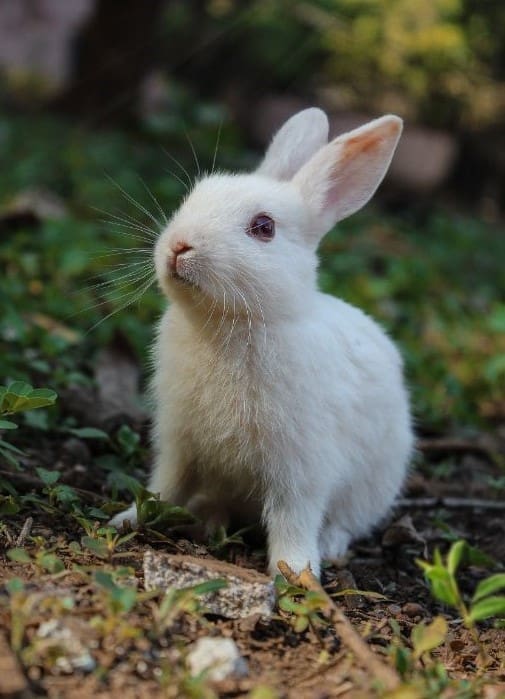
Tularemia is a disease that can affect both animals and humans, with rabbits, hares, and rodents being particularly vulnerable and often dying in large numbers during outbreaks. People can contract the disease through various means, including:
- Tick and deer fly bites
- Skin contact with infected animals
- Drinking contaminated water
- Inhaling contaminated aerosols or dust from agriculture or landscaping
- Laboratory exposure
- Potential bioterrorism-related exposure
Symptoms of tularemia can vary depending on the method of infection. While the disease can be life-threatening, most cases can be successfully treated with antibiotics.
To prevent tularemia, it is recommended to:
- Use insect repellent
- Wear gloves when handling sick or dead animals
- Avoid mowing over deceased animals
Tularemia has been reported in every U.S. state except Hawaii.